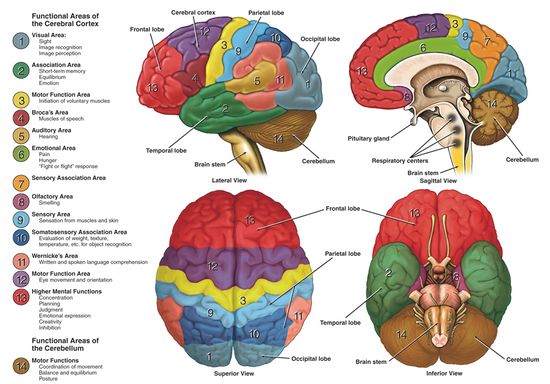
Describe the Function of Each Region of the Cerebral Cortex
Multiple Association areas - describe general function. In summary the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes that are responsible for processing and interpreting input from various sources and maintaining cognitive function.
Multimodal Association Areas make associations between different types of stimuli.

. Creative intuitive spacial emotional sense. The cerebral cortex with all its four lobes is involved in the functions of learning new information forming thoughts language processing making decisions analyzing sensory data and performing memory functions. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
Primary secondary and associative. Anatomically it consists of a series of thin layers consisting of gray matter which are located above a large collection of White matter. Sensory functions interpreted by the cerebral cortex include hearing touch and vision.
The occipital lobe is associated with visual processing. Motor areas allow you to act upon a sensation. Describe the motor area of the cerebral cortex and discuss how it interacts with other parts of the frontal lobe.
Describe the functions of the diencephalon region of the brain. The cerebral cortex can be divided into three basic levels and functions. This functional area helps in coordination of complex movements.
It is also called as gray matter. The frontal lobe occipital lobe parietal lobe and temporal lobe. Each half of the thalamus is about the size and shape of a walnut.
The cortex is extremely convoluted due to which it has a large surface area. The left temporal lobe which is usually the most dominant in people is associated with comprehending language memorizing verbal information forming speech and learning. The dura mater the arachnoid mater and the pia mater.
The right lobe however is associated with memorizing non-verbal information recognizing information and determining facial expressions. This lobe processes and receives information like when someone touches you. A Divided into four regions or lobes.
The exterior portion of the cerebrum is called the cortex or the cerebral mantle. Premotor Cortex plans movements. Upper motor neuron axons project from specific regions of this cortex to specific parts of the body so that a topographic map of the body exists in the primary motor cortex with the head inferior analogous to the.
The frontal lobe is associated with reasoning speech movement emotions problem solving. The four lobes are frontal lobes parietal lobes temporal lobes and occipital lobes. The hierarchically lowest areas are the primary visual auditory somatosensory and motor cortex.
Describe the function of each region of the cerebral cortex. Association areas give meaning tomake associations with a sensation. The cerebrum also includes.
Cognitive functions include thinking perceiving and understanding language. The cerebrum is also in charge of organizing planning and language processing. Motor sensory and associative regions.
This lobes function is to control movement help make decisions solve problems and helps us make our day to day plans in life. In this region functions such as perception imagination thought judgment or decision are performed. The temporal lobe is associated with perception recognition along with memory speech and auditory stimuli.
Cerebral cortex is made up of densely packed neurons that form the outer covering over the cerebral hemispheres. Based on the functions the cerebral cortex contains three regions. The region for problem solving emotion complex thoughts etc is the prefrontal cortex.
Regions of the cerebral cortex that initially process information from the senses. The cerebral cortex is divided into sensory motor and association areas. The parietal lobe is associated.
Each lobe has a different. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system. Hippocampus is among the most important output pathways from the reward and punishment areas of the limbic system.
Levels of cerebral cortex organization. Up to 24 cash back The meninges consist of three layers. Analytical language math sense of direction.
This area helps in. The received information is processed and is sent to the associative regions. This region is related to the perception and recognition of memory auditory stimuli and speech.
This region is responsible for high brain functions like thinking learning and memory. Functional areas of the cerebral cortex. Dura Mater-encases the prain and is the first layer of the brain.
Controls the right side of the body. This lobe helps us with visual processing. Describe the function of each region of the cerebral cortex.
The hippocampus promotes storage of memories. The primary sensory cortex receives information through the thalamus. The sensory nerves end up in the sensory region of the cerebral cortex.
Either of two large ovoid structures of gray matter within the forebrain that relay sensory impulses to the cerebral cortex. In addition this part of the brain is also tasked with interpreting and processing the information obtained from the five senses. A region of the forebrain located below the.
The cortical areas responsible for the elementary functions of either motor or sensory are primary areas. There are four regions in the cerebral cortex. Additionally the cerebral cortex can be divided into three functional areas.
Each lobe has a. Primary Sensory Cortex makes you aware of a sensation. To receive the messages.
Primary area - describe general function. The cerebral cortex is a basic brain area for the functioning of humans. The hippocampus is important in making the decision about which thoughts are important enough on a basis of reward or punishment to be worthy of memory.
Gyrus-a ridge or fold between two clefts on the cerebral surface in the brain. Usually non-doninant controls the left side of the body. BBelow describe each lobe.

Functional Areas Of The Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex Function Basic Anatomy And Physiology

Region Of The Brain That Contains Neurons Involved In Speech Function This Area Located In The Frontal Part Of Brain Anatomy Wernicke S Area Neuroplasticity


0 Response to "Describe the Function of Each Region of the Cerebral Cortex"
Post a Comment